Recent Publications
For a complete list, see my Google Scholar page.
2025
-
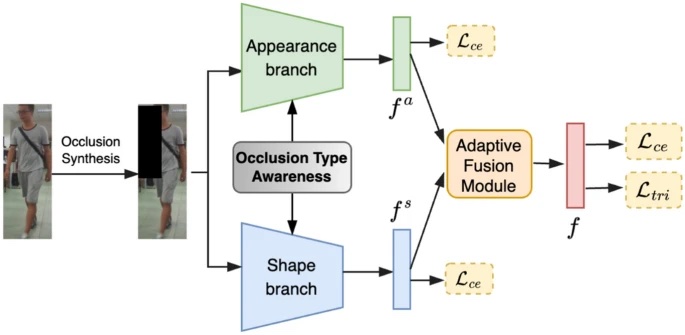 Occlusion-aware appearance and shape learning for occluded cloth-changing person re-identificationVuong D Nguyen, Pranav Mantini, and Shishir K ShahPattern Analysis and Applications, 2025
Occlusion-aware appearance and shape learning for occluded cloth-changing person re-identificationVuong D Nguyen, Pranav Mantini, and Shishir K ShahPattern Analysis and Applications, 2025In recent years, Person Re-Identification (Re-ID) has seen remarkable progress in addressing the issue of clothing changes. However, in real-world scenarios, Re-ID is often further challenged by occlusions, while very little research has been conducted to explicitly tackle these two challenges simultaneously. To this end, we propose a method for Occluded Cloth-Changing Person Re-ID (OCCRe-ID) termed “OASL: Occlusion-aware Appearance and Shape Learning”. OASL introduces a plug-and-play occlusion handling strategy which can be seamlessly integrated into existing Re-ID methods, enabling them to reason discriminative appearance and shape features under occlusions. Specifically, our approach leverages occlusion type information to achieve two key objectives for occlusion-awareness: (1) guide the backbone to focus on extracting identity-aware appearance features from non-occluded image regions and reason features from occluded ones, and (2) recover pose keypoints from occluded regions for mitigating occlusions in shape encoding. Additionally, we construct E-PRCC, the first dataset for OCCRe-ID, with the aim of facilitating further research in this practical domain. Extensive experiments conducted on E-PRCC, LTCC, Occluded-REID, DeepChange, and Market-1501 datasets demonstrate that OASL achieves state-of-the-art performance, offering a robust solution to the dual challenges of occlusions and clothing changes in Person Re-ID.
2024
-
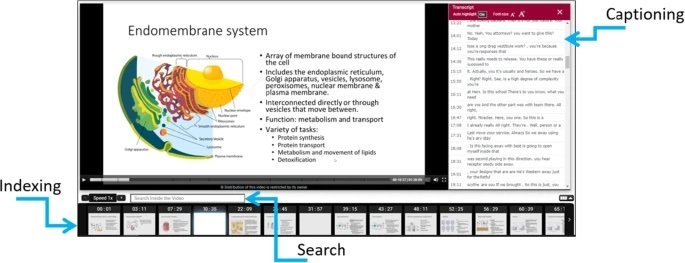 Enhancing lecture video navigation with AI generated summariesMohammad Rajiur Rahman, Raga Shalini Koka, Shishir K Shah, and 2 more authorsEducation and Information Technologies, 2024
Enhancing lecture video navigation with AI generated summariesMohammad Rajiur Rahman, Raga Shalini Koka, Shishir K Shah, and 2 more authorsEducation and Information Technologies, 2024Video is an increasingly important resource in higher education. A key limitation of lecture video is that it is fundamentally a sequential information stream. Quickly accessing the content aligned with specific learning objectives in a video recording of a classroom lecture is challenging. Recent research has enabled automatic reorganization of a lecture video into segments discussing different subtopics. This paper explores AI generation of visual and textual summaries of lecture video segments to improve navigation. A visual summary consists of a subset of images in the video segment that are considered the most unique and important by image analysis. A textual summary consists of a set of keywords selected from the screen text in the video segment by analyzing several factors including frequency, font size, time on screen, and existence in domain and language dictionaries. Evaluation was performed against keywords and summary images selected by human experts with the following results for the most relevant formulations. AI driven keyword selection yielded an F-1 score of 0.63 versus 0.26 for keywords sampled randomly from valid keyword candidates. AI driven visual summary yielded an F-1 score of 0.70 versus 0.59 for K-medoid clustering that is often employed for similar tasks. Surveys showed that 79% (72%) of the users agreed that a visual (textual) summary made a lecture video more useful. This framework is implemented in Videopoints, a real-world lecture video portal available to educational institutions.
- Temporal 3d shape modeling for video-based cloth-changing person re-identificationVuong D Nguyen, Pranav Mantini, and Shishir K ShahIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2024
Video-based Cloth-Changing Person Re-ID (VCCRe-ID) refers to a real-world Re-ID problem where texture information like appearance or clothing becomes unreliable in long-term, limiting the applicability of traditional Re-ID methods. VCCRe-ID has not been well studied primarily due to (1) limited public datasets and (2) challenges related to extracting identity-related clothes-invariant cues from videos. Few existing works have heavily focused on gait-based features, which are severely affected under viewpoint changes and occlusions. In this work, we propose "Temporal 3D ShapE Modeling for VCCRe-ID" (SEMI), a lightweight end-to-end framework that addresses these issues by learning human 3D shape representations. The SEMI framework comprises of a Temporal 3D Shape Modeling branch, which extracts discriminative frame-wise 3D shape features using a temporal encoder, and an identity-aware 3D regressor. This is followed by a novel Attention-based Shape Aggregation (ASA) module that effectively aggregates frame-wise shape features for a fine-grained video-wise shape embedding. ASA leverages an attention mechanism to amplify the contribution of the most important frames while reducing redundancy during the aggregation process. Experiments on two VCCRe-ID datasets demonstrate that our proposed framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 10.7% in rank-1 accuracy and 7.4% in mAP in cloth-changing setting.
- Unsupervised person re-identification in aerial imageryKhadija Khaldi, Vuong D Nguyen, Pranav Mantini, and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2024
The rapidly increasing use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for surveillance has paved the way for advanced image analysis techniques to enhance public safety. Among many others, person re-identification (ReID) is a key task. However, much of the current literature is centered on research datasets, often overlooking the practical challenges and unique requirements of UAV-based aerial datasets. We close this gap by analyzing these challenges, such as viewpoint variations and lack of annotations, and proposing a framework for aerial person re-identification under unsupervised setting. Our framework integrates three stages: generative, contrastive, and clustering, designed to extract view-invariant features for ReID without the need for labels. Finally, we provide a detailed quantitative and qualitative analysis on two UAV-based ReID datasets, and demonstrate that our proposed model outperforms state-of-the-art methods with an improvement of up to 2% in rank-1 scores.
-
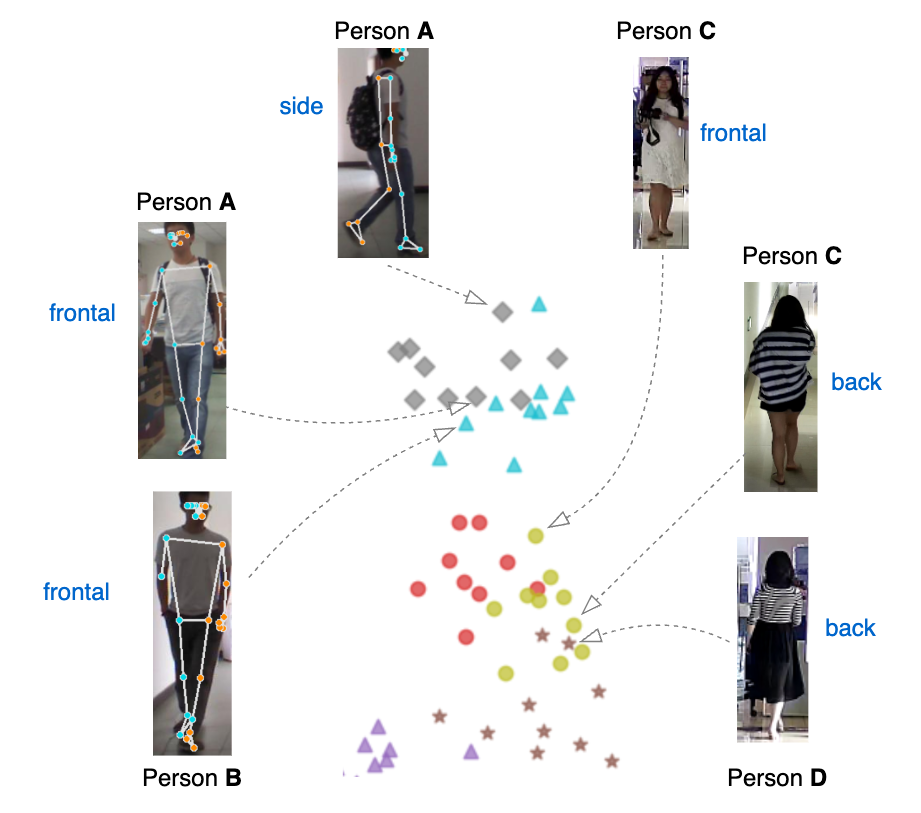 Contrastive viewpoint-aware shape learning for long-term person re-identificationVuong D Nguyen, Khadija Khaldi, Dung Nguyen, and 2 more authorsIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2024
Contrastive viewpoint-aware shape learning for long-term person re-identificationVuong D Nguyen, Khadija Khaldi, Dung Nguyen, and 2 more authorsIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2024Traditional approaches for Person Re-identification (Re-ID) rely heavily on modeling the appearance of persons. This measure is unreliable over longer durations due to the possibility for changes in clothing or biometric information. Furthermore, viewpoint changes significantly degrade the matching ability of these methods. In this paper, we propose "Contrastive Viewpoint-aware Shape Learning for Long-term Person Re-Identification" (CVSL) to address these challenges. Our method robustly extracts local and global texture-invariant human body shape cues from 2D pose using the Relational Shape Embedding branch, which consists of a pose estimator and a shape encoder built on a Graph Attention Network. To enhance the discriminability of the shape and appearance of identities under viewpoint variations, we propose Contrastive Viewpoint-aware Losses (CVL). CVL leverages contrastive learning to simultaneously minimize the intra-class gap under different viewpoints and maximize the inter-class gap under the same viewpoint. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods on long-term person Re-ID benchmarks.
- Contrastive clothing and pose generation for cloth-changing person re-identificationVuong D Nguyen, Pranav Mantini, and Shishir K ShahIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2024
Cloth-Changing Person Re-Identification (CCRe-ID) aims at matching an individual across cameras after a long period of time presenting variations in clothing compounded with changes in pose viewpoint etc. In this work we propose CCPG: Contrastive Clothing and Pose Generation framework for CCRe-ID. Beyond appearance CCPG captures cloth-invariant body shape information using a Relational Graph Attention Network. Training a robust CCRe-ID model requires a large range of clothing variations and expensive cloth labeling which is lacked in current CCRe-ID datasets. To address this we propose a GAN-based model for clothing and pose transfer across identities to augment images of wider clothing variations and of different persons wearing similar clothing. The augmented batch of images serve as inputs to our proposed Fine-grained Contrastive Losses which not only supervise the Re-ID model to learn discriminative person embeddings under long-term scenarios but also ensure in-distribution data generation. Results on CCRe-ID datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our CCPG framework. Code will be available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CCPG-ReID.
- Tackling domain shifts in person re-identification: A survey and analysisVuong D Nguyen, Samiha Mirza, Abdollah Zakeri, and 6 more authorsIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2024
The necessity for a Person ReID system for rapidly evolving urban surveillance applications is severely challenged by domain shifts-variations in data distribution that occur across different environments or times. In this paper we provide the first empirical review of domain shift in person ReID which includes three settings namely Unsupervised Domain Adaptation ReID Domain Generalizable ReID and Lifelong ReID. We observe that existing approaches only tackle domain shifts caused by cross-dataset setting while ignoring intra-dataset attribute domain shifts caused by changes in clothing shape or gait which is very common in ReID. Thus we enhance research directions in this field by redefining domain shift in ReID as the combination of attribute domain shift with cross-dataset domain shift. With a focus on Lifelong Re-ID methods we conduct an extensive comparison on a fair experimental setup and provide an in-depth analysis of these methods under both non-cloth-changing and cloth-changing Re-ID scenarios. Insights into the strengths and limitations of these methods based on their performance are studied. This paper outlines future research directions and paves the way for the development of more adaptive resilient and enduring cross-domain ReID systems. Code is available at https://github.com/dustin-nguyen-qil/Lifelong-CC-ReID.
- Occluded cloth-changing person re-identification via occlusion-aware appearance and shape reasoningVuong D Nguyen, Pranav Mantini, and Shishir K ShahIn 2024 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), 2024
Existing methods in Person Re-Identification (ReID) often fail when simultaneously confronted with occlusions and clothing changes. In this paper, we introduce a challenging yet practical task called Occluded Cloth-Changing Re-ID (OCCRe-ID/). We propose Occlusion-aware Appearance and Shape Reasoning, the first framework OCCReID. We first propose an occlusion synthesis strategy to expose the model to real-world occlusion variations. We mitigate clothing changes by coupling silhouette-based body shape information with appearance. Unlike previous works that directly leverage unreliable features extracted from occluded images by off-the-shelf backbones, we propose an occlusion-awareness strategy to handle occlusions for ReID. An occlusion detection module is elaborately designed to generate occlusion-aware feature, which is then used to guide the framework to reason robust appearance and shape features. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our framework over both cloth-changing Re-ID and occluded Re-ID methods.
-
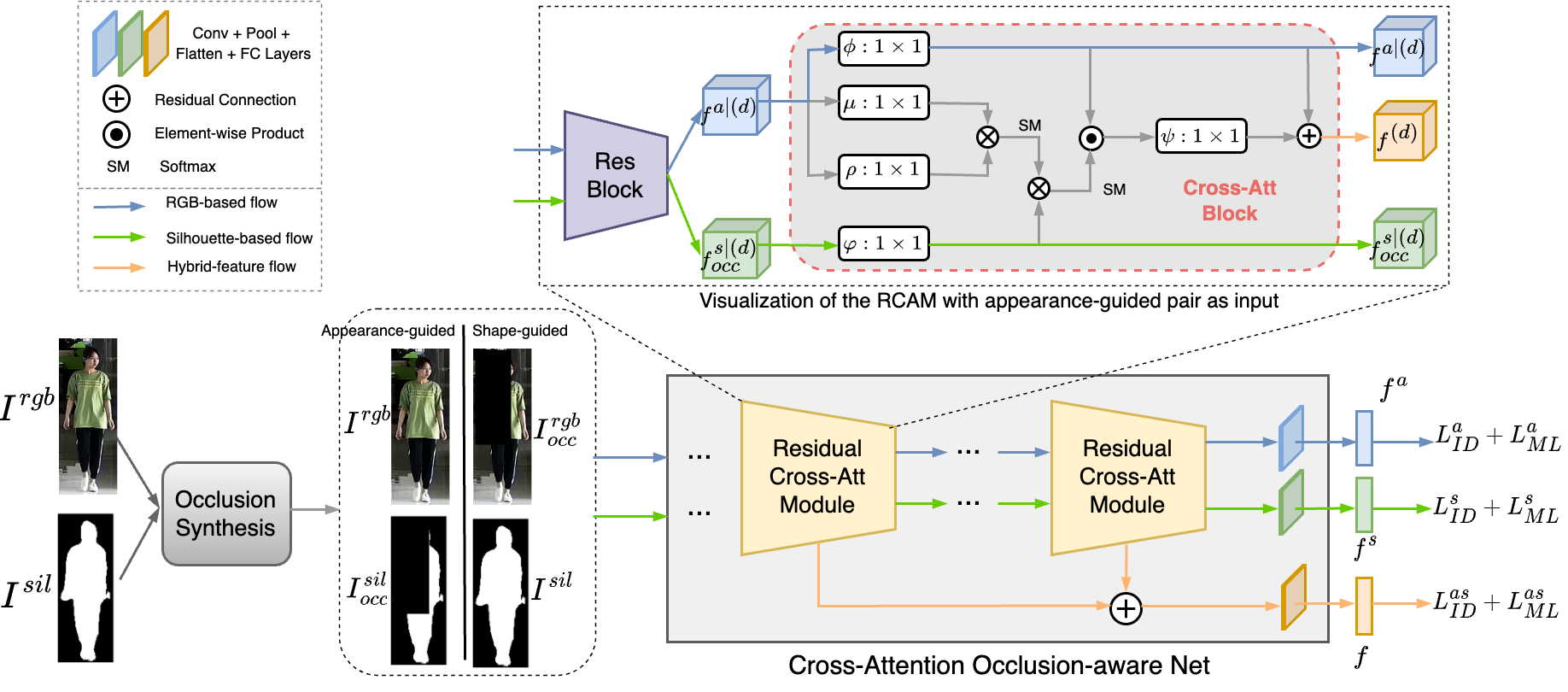 ACML: Attention-based cross-modality learning for cloth-changing and occluded person re-identificationVuong D Nguyen, Pranav Mantini, and Shishir K ShahIn 2024 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2024
ACML: Attention-based cross-modality learning for cloth-changing and occluded person re-identificationVuong D Nguyen, Pranav Mantini, and Shishir K ShahIn 2024 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2024Person Re-Identification (Re-ID) aims at matching a person captured by a non-overlapping camera system. Real-world Re-ID presents challenges like clothing changes and occlusions, which limits the applicability of traditional appearance-based methods. Cloth-Changing Re-ID (CCRe-ID) methods that rely on cloth-invariant modalities, such as shape, gait, etc., ignore occlusions and fail to mine the complementary relationship across modalities. Meanwhile, methods that explicitly focus on occlusion management struggle with cloth-changing scenarios. To address these, we propose ACML: Attention-based Cross-Modality Learning, the first framework to tackle both clothing changes and occlusion in Re-ID. Our lightweight framework comprises a unified network with cascaded Cross-Attention Blocks that extracts appearance and shape features collaboratively, enhancing robustness under clothing changes, viewpoint variations, and poor illumination conditions. Inputs to the network are produced by our novel occlusion synthesis module, which not only helps exposing the model to occlusions but also guides the model to adaptively attend to informative cues and reduce noise. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of ACML on both CCRe-ID and occluded Re-ID datasets.
- Occlusion-aware Cross-Attention Fusion for Video-based Occluded Cloth-Changing Person Re-IdentificationVuong D Nguyen, Pranav Mantini, and Shishir K ShahIn 2024 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), 2024
Video-based Person Re-Identification (Re-ID) is an important task in video surveillance analysis. Real-world video-based Re-ID commonly suffers from clothing changes and occlusions, which severely degenerates performance of traditional Re-ID methods. In this paper, we introduce a challenging yet practical task called Video-based Occluded Cloth-Changing Re-ID (VOCCRe-ID). To tackle occlusions, we propose an occlusion synthesis strategy to expose the model to real-world occlusion variations. To mitigate unreliable appearance caused by clothing changes, we couple body shape information from the normalized silhouette sequence. Then, we propose a cross-attention fusion mechanism to capture the complementary relationships between appearance and shape under occlusions, thus enhancing Re-ID robustness. In addition, since there are no dataset for VOCCRe-ID, we build the large-scale Occluded-VCCR dataset which explicitly presents occlusions and contains the most clothing variations. Extensive experiments show that we achieve SOTA performance over previous methods.
-
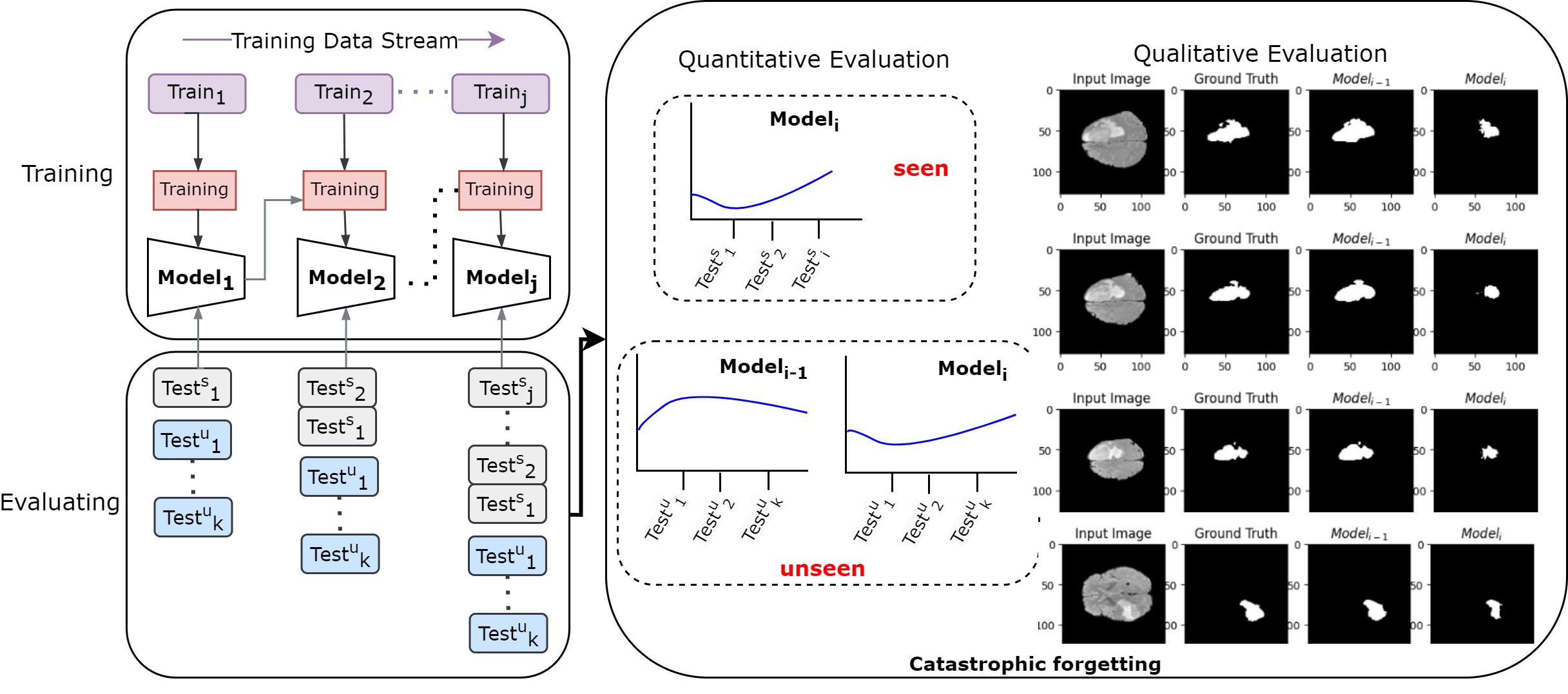 Recall-Based Knowledge Distillation for Data Distribution Based Catastrophic Forgetting in Semantic SegmentationSamiha Mirza, Apurva Gala, Pandu Devarakota, and 3 more authorsIn International Conference on Pattern Recognition, 2024
Recall-Based Knowledge Distillation for Data Distribution Based Catastrophic Forgetting in Semantic SegmentationSamiha Mirza, Apurva Gala, Pandu Devarakota, and 3 more authorsIn International Conference on Pattern Recognition, 2024Semantic segmentation involves labeling each pixel in an image with a corresponding class label, enabling detailed scene understanding. In dynamic environments, where conditions change over time, incremental learning techniques are essential for updating segmentation models with newly acquired data. However, incremental segmentation faces the challenge of catastrophic forgetting, where models lose previously learned knowledge when trained on new data distributions. To address this, we propose a recall-based knowledge distillation approach for stable segmentation model training across dynamic environments. Our method combines the strengths of knowledge distillation and recall learning to enhance the model’s ability to recall information from previous data distributions while adapting to new ones. By reintroducing a small portion of the previous dataset during training and applying tailored distillation techniques, our approach mitigates catastrophic forgetting and improves the robustness of these models. Through comprehensive evaluations, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in two scenarios: salt segmentation in seismic datasets and tumor segmentation in MRI datasets. Our method offers a promising solution for addressing the challenges of catastrophic forgetting in incremental semantic segmentation, facilitating the development of more adaptive and reliable computer vision systems in dynamic environments.
- CrossViT-ReID: Cross-Attention Vision Transformer for Occluded Cloth-Changing Person Re-IdentificationVuong D Nguyen, Pranav Mantini, and Shishir K ShahIn Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, 2024
Real-world Person Re-Identification (Re-ID) presents severe challenges like occlusions and clothing changes, making traditional Re-ID methods fail. Existing occluded Re-ID methods struggle with cloth-changing scenarios, while current cloth-changing Re-ID methods do not explicitly address occlusions. To this end, we propose CrossViT-ReID, the first framework for the challenging yet practical Occluded Cloth-Changing Person Re-ID task. We perform occlusion synthesis to expose the model to real-world occlusion variations, and capture cloth-invariant body shape modality from silhouettes. The key to success of CrossViT-ReID lies in our novel cross-modality collaborative training strategy which is capable of mining the complementary relationship between appearance and shape adaptively under occlusions, clothing changes, or bad lighting conditions. Specifically, we devise two identical ViT-based branches. One branch takes in holistic appearance and occluded shape, aiming to focus on appearance when shape is noisy. Meanwhile, occluded appearance and holistic shape are inputs to the other branch, aiming to attend to shape when appearance is partly unobservable. Cross attention fusion then makes the two branches exchange beneficial information and complement each other. After being trained, our framework is able to amplify the most informative cues when facing ambiguity caused by in-the-wild Re-ID challenges, thus significantly enhancing Re-ID accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of CrossViT-ReID on both cloth-changing Re-ID and occluded Re-ID datasets.
- Cross-Modality Complementary Learning for Video-Based Cloth-Changing Person Re-identificationVuong D Nguyen, Pranav Mantini, and Shishir K ShahIn Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, 2024
Video-based Cloth-Changing Person Re-ID (VCCRe-ID) is a real-world Re-ID problem where individuals are observed in settings with a high likelihood of clothing changes between observations. To tackle this problem, capturing cloth-invariant modalities remains more effective than texture-based approaches. However, previous works extracted these modalities separately and directly leveraged the learned features for Re-ID, which is not effective since viewpoint changes and occlusion cause severe ambiguity in these modalities. To address this limitation, we propose a dual-branch framework that couples cloth-invariant modalities (i.e. shape and gait) with appearance by novelly exploiting the complementary relationship across them. In this work, we design a texture branch that enables body shape to complement the ambiguity in appearance caused by illumination variations or occlusions. Then texture and gait features are mutually learned at multiple levels, which helps to exchange beneficial information across branches for more discriminative person representations. We build a large-scale video-based cloth-changing dataset that contains the most cloth variations and is the first benchmark that mimics the real-world similar-clothing scenario. Extensive experiments show that our proposed framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods by a large margin. Code and dataset will be available at https://github.com/dustin-nguyen-qil/CCL-VCCReID.
2023
-
 Object measurementFatima A Merchant, Shishir K Shah, and Kenneth R CastlemanIn Microscope Image Processing, 2023
Object measurementFatima A Merchant, Shishir K Shah, and Kenneth R CastlemanIn Microscope Image Processing, 2023Microscope Image Processing, Second Edition, introduces the basic fundamentals of image formation in microscopy including the importance of image digitization and display, which are key to quality visualization. Image processing and analysis are discussed in detail to provide readers with the tools necessary to improve the visual quality of images, and to extract quantitative information. Basic techniques such as image enhancement, filtering, segmentation, object measurement, and pattern recognition cover concepts integral to image processing. In addition, chapters on specific modern microscopy techniques such as fluorescence imaging, multispectral imaging, three-dimensional imaging and time-lapse imaging, introduce these key areas with emphasis on the differences among the various techniques.
- Identification of Visual Objects in Lecture Videos with Color and Keypoints AnalysisDipayan Biswas, Shishir Shah, and Jaspal SubhlokIn 2023 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia (ISM), 2023
Recorded lecture videos are an increasingly important learning resource. However, traditional video format does not allow quick navigation to the desired content of interest. Recent research has enhanced navigation by dividing lecture videos into chapters and creating a summary of each chapter. The visual content on lecture video frames represents a valuable source of information for identifying topic boundaries as well as summarizing content. The focus of the research presented in this paper is to accurately identify visual objects in lecture video frames. The methods developed for camera videos are not directly applicable here as the visual content includes charts, graphs, and illustrations intermingled with text. A common approach based on locating regions with continuous pixel changes has a key limitation that logically consistent visual objects can have modest size gaps inside them. The result is over-segmentation, where a logical object is split into multiple objects if the gap threshold is too low, or under-segmentation, where adjacent objects are recognized as a single large object if the gap threshold is too high. This paper introduces a novel approach that exploits the observation that components of logical objects often have color and geometrical similarity. In our methodology, first a relatively large number of visual elements are identified with a small gap threshold. Subsequently, these visual elements are selectively combined using gap along with color and geometrical similarity. An evaluation was conducted with a suite of 170 lecture video frames from STEM coursework. The results demonstrate the significant impact of color and geometry in improving the accuracy of visual object identification in lecture video frames.